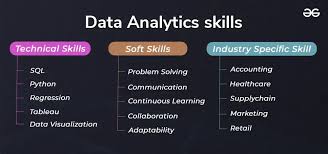
Learn Data Analysis Skills for Marketing Professionals
In today’s data-driven world, marketing professionals must possess strong data analysis skills to stay ahead of the competition. Understanding consumer behavior, optimizing campaigns, and measuring return on investment (ROI) all require data-driven decision-making. This guide will introduce marketing professionals to essential data analysis skills and techniques to help them make informed business decisions.
Why Data Analysis is Crucial for Marketing Professionals
Marketing is no longer just about creativity; it is about making informed choices based on data insights. Here are some reasons why data analysis is essential in marketing:
- Understanding Customer Behavior: Analyzing customer interactions helps businesses understand their preferences, behaviors, and purchasing patterns.
- Campaign Optimization: Data-driven insights help marketers refine their strategies, ensuring better engagement and conversion rates.
- Measuring ROI: Proper data analysis allows businesses to track the effectiveness of their marketing efforts, ensuring they allocate budgets efficiently.
- Competitive Advantage: Businesses that use data effectively can gain a competitive edge by identifying market trends and consumer demands.
Key Data Analysis Skills for Marketing Professionals
To excel in data-driven marketing, professionals should develop the following skills:
1. Data Collection and Management
Before analyzing data, marketing professionals must know how to collect and manage it. Common sources of marketing data include:
- Website analytics tools (e.g., Google Analytics)
- Social media insights (e.g., Facebook Insights, Twitter Analytics)
- Customer relationship management (CRM) systems
- Surveys and feedback forms
- Email marketing software (e.g., Mailchimp, HubSpot)
2. Data Cleaning and Preparation
Raw data often contains errors, duplicates, or missing values. Cleaning and preparing data ensure accuracy and reliability. Essential data cleaning techniques include:
- Removing duplicate entries
- Filling in missing data or removing incomplete records
- Standardizing data formats
- Filtering out irrelevant data points
3. Statistical Analysis
Basic statistical knowledge helps marketers make sense of data trends and patterns. Important statistical concepts include:
- Mean, median, and mode
- Standard deviation
- Correlation and regression analysis
- A/B testing
4. Data Visualization
Presenting data in an understandable format is crucial for decision-making. Marketing professionals should be proficient in:
- Creating graphs and charts (e.g., bar charts, line graphs, pie charts)
- Using tools like Tableau, Google Data Studio, or Microsoft Power BI
- Interpreting visual data insights
5. Predictive Analytics and Machine Learning
Predictive analytics uses historical data to forecast future trends. Machine learning techniques can help marketers automate and enhance decision-making. Some applications include:
- Customer segmentation and targeting
- Predicting customer churn
- Recommender systems (e.g., personalized product recommendations)
6. Web and Social Media Analytics
Understanding website and social media performance is essential for marketers. Important metrics include:
- Website traffic and page views
- Bounce rates and session durations
- Social media engagement (likes, shares, comments)
- Conversion rates
7. SQL and Database Management
Structured Query Language (SQL) is useful for retrieving and analyzing large datasets. Marketing professionals can use SQL to:
- Extract specific customer data
- Identify trends in purchasing behavior
- Automate data reporting processes
8. Marketing Attribution and ROI Analysis
Marketing attribution models help professionals determine which channels contribute most to conversions. Common attribution models include:
- First-touch attribution
- Last-touch attribution
- Multi-touch attribution
- Time-decay attribution
Tools for Data Analysis in Marketing
Marketing professionals can leverage various tools to analyze data effectively:
- Google Analytics: For tracking website traffic and user behavior.
- Microsoft Excel: For data cleaning, visualization, and statistical analysis.
- Tableau and Power BI: For creating interactive data visualizations.
- Google Data Studio: For building marketing reports.
- Python and R: For advanced data analysis and machine learning.
- HubSpot and Salesforce: For CRM and marketing automation.
Practical Applications of Data Analysis in Marketing
1. Customer Segmentation
By analyzing demographic, geographic, and behavioral data, marketers can segment customers and create personalized marketing campaigns.
2. Content Performance Analysis
Marketers can track which blog posts, videos, or social media posts drive the most engagement and optimize future content accordingly.
3. Email Marketing Optimization
Analyzing email open rates, click-through rates, and conversion rates helps marketers refine their email marketing strategies.
4. PPC Campaign Performance Tracking
Pay-per-click (PPC) campaigns generate valuable data on cost-per-click (CPC), click-through rates (CTR), and ad conversion rates, allowing for better ad spend optimization.
5. Social Media Strategy Enhancement
Marketers can analyze social media engagement metrics to determine which content resonates best with their audience and adjust their strategy accordingly.
Conclusion
Incorporating data analysis into marketing strategies empowers professionals to make data-driven decisions, optimize campaigns, and improve customer engagement. By developing skills in data collection, statistical analysis, visualization, and predictive analytics, marketing professionals can stay competitive in the digital landscape. With the right tools and knowledge, marketers can turn raw data into actionable insights that drive business success.